Generating a random number is a common task in Python, especially when you are working on a Statistics or Machine Learning project.
In this article, I will show you how to generate random numbers in Python using the random module with 5 most common use cases that you will encounter most of the time.
Contents
- Generating a Random Number Between 0 and 1
- Generating a Random Number Between Two Numbers
- Generating a Random Integer Between Two Numbers
- Generating a List of Random Numbers
- Generating a List of Random Integers using
random.sample - Conclusion
Generating a Random Number Between 0 and 1
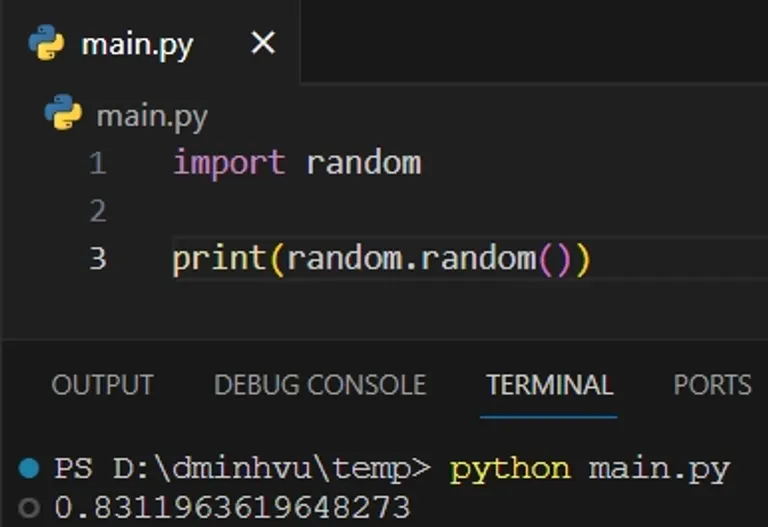
To generate a random number between 0 and 1 in Python, you can use the random.random function.
import random print(random.random())
The output will be a random number between 0 and 1.
0.8311963619648273
Generating a Random Number Between Two Numbers
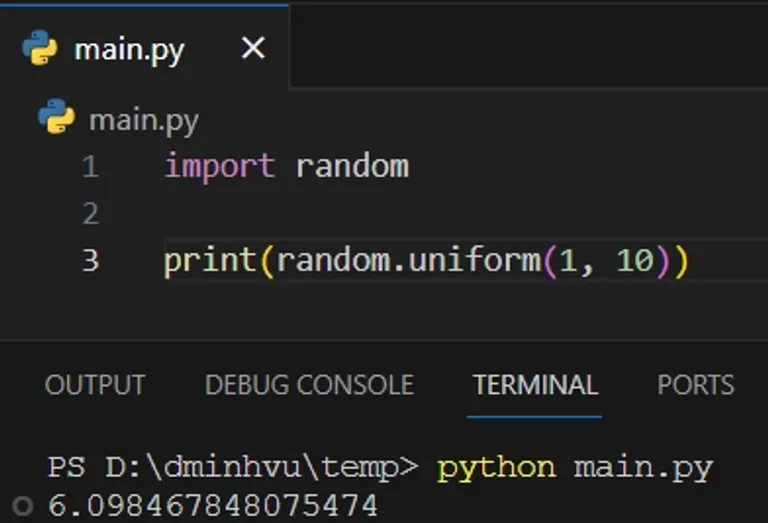
To generate a random number between two numbers in Python, you can use the random.uniform function.
For example, to generate a random number (including real numbers) between 1 and 10, you can use the following Python code:
import random print(random.uniform(1, 10))
The output will be a random number between 1 and 10 based on the uniform distribution.
6.098467848075474
Generating a Random Integer Between Two Numbers
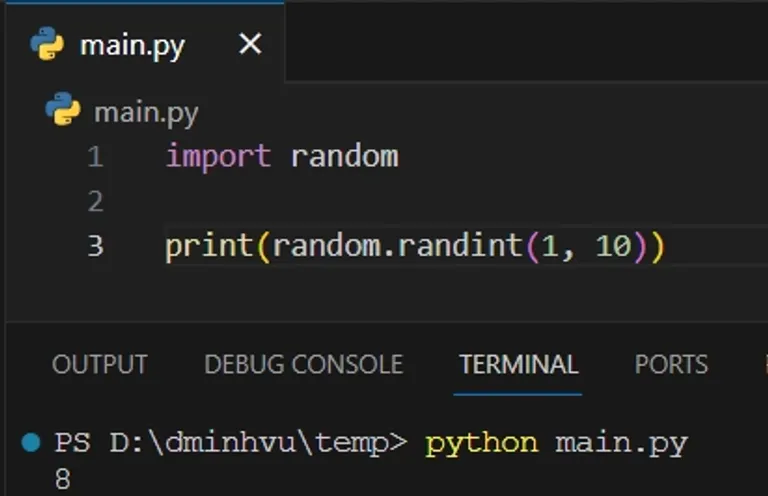
To generate a random integer between two numbers, you can use the random.randint function.
For example, to generate a random integer between 1 and 10, you can use the following Python code:
import random print(random.randint(1, 10))
The output will be a random integer between 1 and 10.
8
Generating a List of Random Numbers
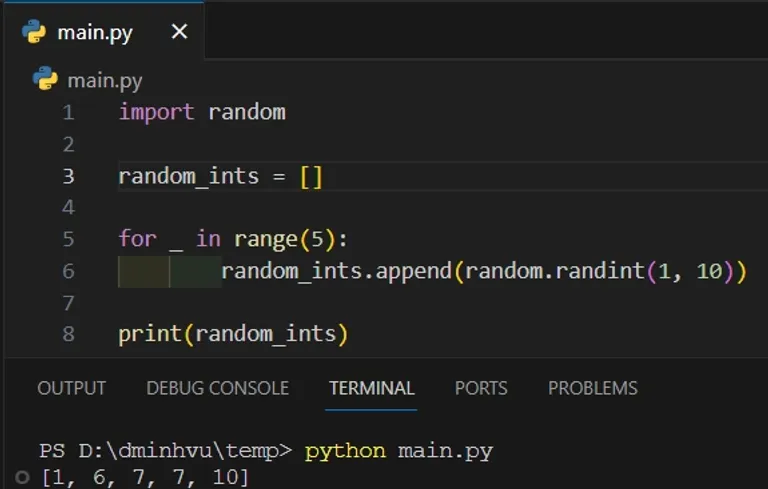
To generate a list of random numbers in Python, you can use a for loop and put the above random functions inside it.
For example, to generate 5 random integers between 1 and 10, you can use the following Python code:
import random random_ints = [] for _ in range(5): random_ints.append(random.randint(1, 10)) print(random_ints)
We get 5 random integers between 1 and 10.
[1, 6, 7, 7, 10]
Generating a List of Random Integers using random.sample
Another way to generate a list of random integers in Python is to use the random.sample function.
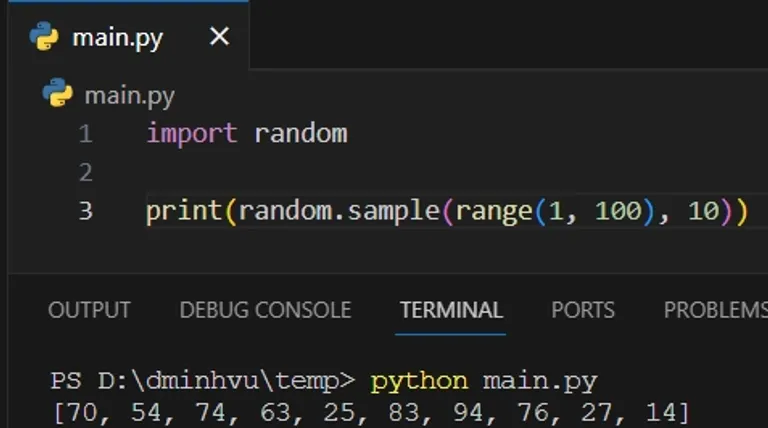
For example, to generate 10 random integers between 1 and 100, you can use the following Python code:
import random print(random.sample(range(1, 100), 10))
The output will be a list of 5 random integers between 1 and 10.
[70, 54, 74, 63, 25, 83, 94, 76, 27, 14]
Conclusion
There are 5 common use cases when you want to generate random numbers in Python:
- Generate a random number between 0 and 1:
random.random() - Generate a random number between two numbers:
random.uniform(a, b) - Generate a random integer between two numbers:
random.randint(a, b) - Generate a list of random numbers: use a
forloop with the above functions - Generate a list of random integers:
random.sample(range(a, b), n)

Comments
Be the first to comment!